synchornized关键字用于控制同步,它修饰的对象主要有以下几种:
- 修饰一个代码块,称为同步语块,其作用是获取某个对象或类的锁,直到同步语块结束释放锁
- 修饰一个方法,被修饰的方法称为同步方法,其作用是获取
this对象的锁,直至方法运行结束释放锁
- 修饰一个静态方法,其作用是获取类锁,直至方法运行结束释放锁
修饰代码块
synchornized(this) 线程调用对象自身的锁,其他试图获取该对象锁的线程被阻塞。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| public class Sync {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SyncThread syncThread = new SyncThread();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(syncThread, "SyncThread1");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(syncThread, "SyncThread2");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
class SyncThread implements Runnable {
private int count;
public SyncThread() {
count = 0;
}
public void run() {
synchronized(this) {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + (count++));
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
}
|
运行结果如下,线程1运行时,需要获取同一对象锁的线程2被阻塞
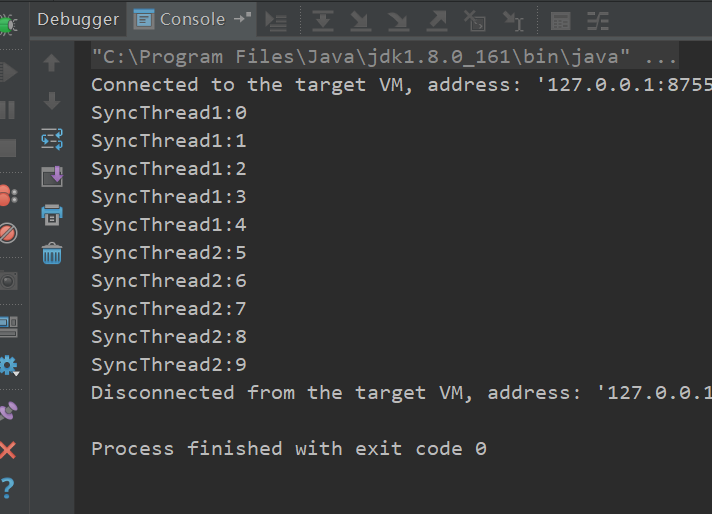
**如果两个线程获取的不是同一对象的锁,则不会发生阻塞:**
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public class Sync {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SyncThread syncThread = new SyncThread();
SyncThread syncThread1 = new SyncThread();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(syncThread, "SyncThread1");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(syncThread1, "SyncThread2");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
|
其他线程任然可以运行该线程的非synchornized方法, 因为调用那些方法的线程,并没有尝试去获取该对象的锁:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
| public class Sync {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SyncThread syncThread = new SyncThread();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(syncThread, "SyncThread1");
thread1.start();
syncThread.getCount();
}
}
class SyncThread implements Runnable {
private int count;
public SyncThread() {
count = 0;
}
public void run() {
synchronized(this) {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + (count++));
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public void getCount() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + (count++));
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
|
运行结果如下,并未发生阻塞:
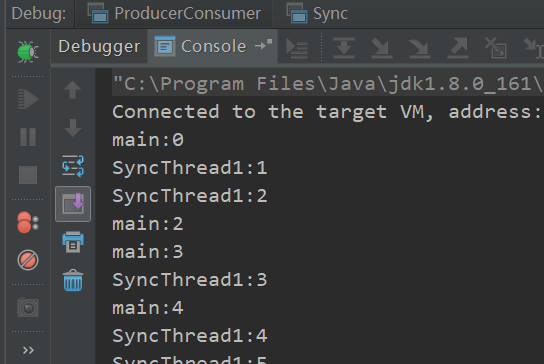
synchornized(object) 线程获得某对象的锁,其他试图获取该对象锁的线程被阻塞。
同上一条。
synchornized(xxx.class) 线程获得该类的锁,其他试图获取该类锁的线程被阻塞。
将上个例子改为如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| class SyncThread implements Runnable {
private int count;
public SyncThread() {
count = 0;
}
public void run() {
synchronized(SyncThread.class) {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + (count++));
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
}
|
运行结果如下:
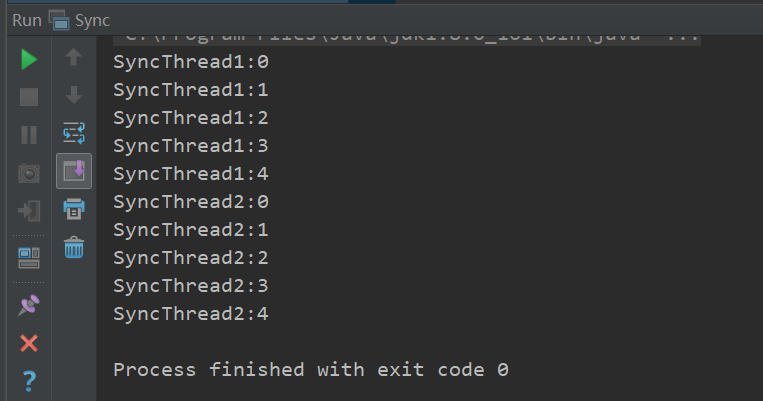
对于要获取同一对象锁的线程1和2会发生阻塞。
修饰方法
修饰非静态方法, 线程获取对象的锁,其他尝试获取该对象锁的线程都会被阻塞
情况同对象锁同步代码块。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
|
public class Sync {
public static void main(String[] args) {
c c = new c();
SyncThread syncThread = new SyncThread(c);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(syncThread, "SyncThread1");
thread1.start();
c.d(0);
}
}
class SyncThread implements Runnable {
private int count;
private c x;
public SyncThread(c x) {
count = 0;
this.x = x;
}
public void run() {
synchronized(x) {
x.c(count++);
}
}
}
class c {
public void c(int count) {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + (count));
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public synchronized void d(int count) {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + (count++));
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
|
运行结果显示会发生阻塞,因为main线程和SyncThread1尝试去获取同一对象的锁,必然有一个线程发生阻塞。
修饰静态方法,线程获取类的锁,其他尝试获取类的锁的线程被阻塞
情况同类锁同步代码块


